Portuguese EEZ - Exploitation
Fishing is a traditional activity in Portugal. The fishery is predominated by small, local fishing vessels. Over the past decades the number of ships has decreased, but this has been compensated by an increase in power per vessel. The small scale artisanal fleet (vessels less than 12 m) is most important in terms of numbers, while the artisanal fleet over 12 m is the most important in terms of Gross Tonnage (Table 1). Portuguese fisheries are managed in accordance with the European Common Fisheries Policy, which includes TACs and quotas for some species, fishing area or gear restrictions, minimum size requirements for captures, standard mesh sizes, and maximum percentages of incidental catches.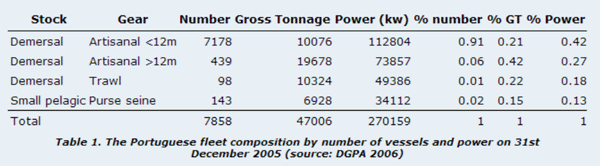
In 2005, the total landings for the Portuguese fleet were 128 943.70 tonnes, of which 42% was caught by purse seines, 17% by trawls and 41% by polyvalent fleets. The purse seine fishery targets mainly sardine, but also captures horse mackerel, chub mackerel and mackerel in smaller quantities. Sardine is the most important species in terms of total landings in Portugal. In 2005, sardine accounted for 46% of total landings of all species. The average value of the sardine fishery was only 0.65 euros compared to 1.25 euros for the entire fishery. The most valuable species caught in Portuguese waters are seabream (Pagrus pagrus) and striped red mullet (Mullus surmuletus), but these only represent about 0.10% of total landings each.
There are two distinct trawl fisheries in Portugal. One targets fish and cephalopods, and the other targets crustaceans. The main species caught by the trawl fishery targeting fish are Atlantic horse mackerel, blue whiting, octopus and hake. Although the trawl fleet that targets crustaceans is small, it is a lucrative fishery. The main species captured are red shrimp and deepwater rose shrimp.
The polyvalent or artisanal fleet is made up of boats that are licensed to use several different gear types throughout the year. These boats operate in both coastal waters (smaller boats less than 12 m) and further offshore. The main gears used are gillnets, trammel and longlines. The most important species in terms of weight caught by the artisanal fishery is octopus, caught in pots and traps.
