Mauritanian EEZ
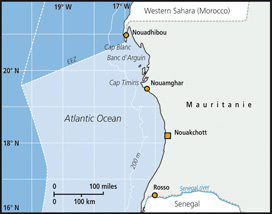
The introduction of many fishing boats to the industrial fisheries in the early 1980s resulted in increased catches of pelagic and demersal species, which led to a decline in the abundance of some 20 species, mainly demersal fish and cephalopods. Long-term trends (1980-2005) confirm a significant decline in trophic level of landings and inverse fishing pressure. Most short-term trends (1996-2005) are negative though not significant. A recent yearly seasonal break in fishing activities was initiated, aimed to reduce fishing intensity. No short term effects of this attempt to diminish the detrimental impacts of fishing have been detected. Comparing the recent ecosystem state of Mauritania to other ecosystems shows that 4 state indicators are at very low levels. |
SST = Sea Surface Temperature (°C) 
|
