Barents Sea - Geographic area
 The Barents Sea was defined as Subarea I by FAO to be within these boundaries:
The Barents Sea was defined as Subarea I by FAO to be within these boundaries:
“The waters bounded by a line from the geographic North Pole along the meridian of 30°00' east longitude to 72°00' north latitude; thence due west to 26°00' east longitude; thence due south to the coast of Norway; thence in an easterly direction along the coasts of Norway and the USSR to Khaborova; thence across the western entry of the Strait of Yugorskiy Shar; thence in a westerly and northerly direction along the coast of Vaigach Island; thence across the western entry of the Strait of the Karskiye Vorota; thence west and north along the coast of the south island of Novaya Zemlya; thence across the western entry of the Strait of Matochkin Shar; thence along the west coast of the north island of Novaya Zemlya to a point at 68°30' east longitude; thence due north to the geographic North Pole.” In May 2013 the Arctic council revised the boundaries of the Arctic, The boundary has been changed to include the Lofoten Islands in the Barents Sea LME. This region is the main spawning area of the Barents Sea cod stock which is a major component of this ecosystem. The boundary has further been shifted west to include the upper slope region from the Barents Sea into the Norwegian Sea as part of the Barents Sea LME. There is a current of Atlantic water flowing north along the slope in this region which hold the main spawning areas for Greenland halibut and other fishes that are trophically linked and parts of the Barents Sea LME. (Skjoldal and Pundy 2013).
The western boundary to the Norwegian Sea is from 67.5 N across the Vestfjord and then north to the shelf edge off Vesterålen. The justification for including this part of the Norwegian Shelf in the Barents Sea LME is that this includes the main spawning areas of the Barents Sea cod stock in the Lofoten area. The boundary continues north along the slope to the Norwegian Sea so that the slope where the Atlantic water flows north along Spitsbergen is included as part of the Barents Sea LME. The slope off the Barents shelf is the main spawning area for Greenland halibut which is a major species in the Barents Sea LME. The boundary continues north along the western slope of the Yarmak Plateau in the Fram Strait region to about 83oN. The boundary continues east into the Arctic Ocean so that the slope from the Barents shelf where the Atlantic water flows is included as part of the Barents Sea LME. The northeastern boundary to the Kara Sea LME is a line from the northern tip of Novaya Zemlya passing just east of the Franz Josef Land archipelago. This is a fairly open ecosystem boundary without a clear distinguishing topographic or oceanographic feature. The southeastern boundary to the Kara Sea LME is at the narrow Kara Gate south of Novaya Zemlya. The White Sea is included as a part of the Barents Sea LME.
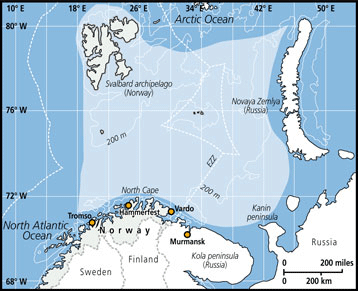
The Indiseas 2 data is collected from surveys in the sub-Arctic ecosystem located between 68 and 82ºN, where the data for Indiseas 2 is collected. The east-west boundaries for the surveys are 3ºE and 69 ºE, covering an area of 1.4 mill. km2.
The Barents Sea connects with the Norwegian Sea to the west and the Arctic Ocean to the north. The Barents Sea is within the FAO major fishing area 27, corresponding to ICES fishing areas Ia, Ib, the western part of IIb2 and the northern part of IIa2).
FAO Fishing Areas: [ 27.I ; 27.IIb ]
